——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Synthesizer #Mozzi #Keyboard #ADSREnvelope #Arduino #ArduinoProMini #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Envelope (Music)
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. It may relate to elements such as amplitude (Volume), frequencies (with the use of filters) or pitch. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero.
Envelope generators, which allow users to control the different stages of a sound, are common features of synthesizers, samplers, and other electronic musical instruments. The most common form of envelope generator is controlled with four parameters: attack, decay, sustain and release (ADSR).
A Simple ADSR Envelope Generator
This implementation has separate update() and next() methods, where next() interpolates values between each update(). The “normal” way to use this would be with update() in updateControl(), where it calculates a new internal state each control step, and then next() is in updateAudio(), called much more often, where it interpolates between the control values. This also allows the ADSR updates to be made even more sparsely if desired, eg. every 3rd control update.
noteOn()
Start the attack phase of the ADSR. This will restart the ADSR no matter what phase it is up to. True, the envelope will start from 0, even if it is still playing, often useful for effect envelopes. If false, the envelope will start rising from the current level, which could be non-zero, if it is still playing, most useful for note envelopes.
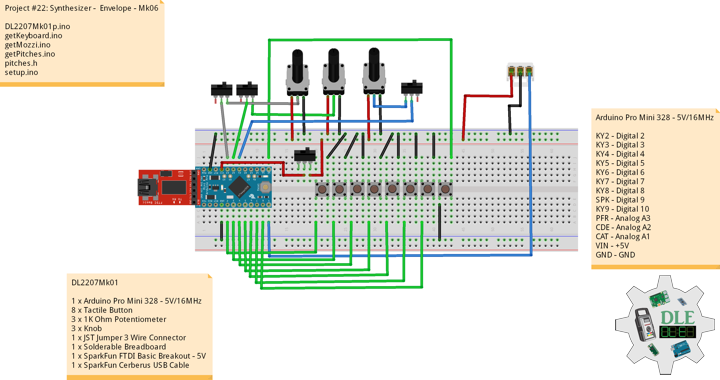
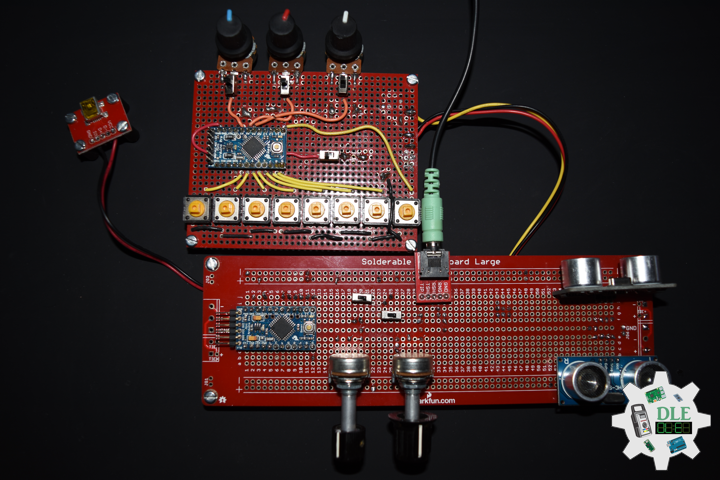
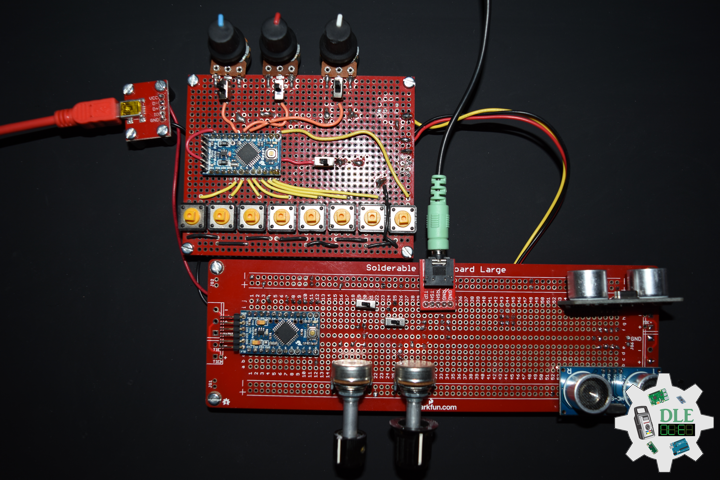
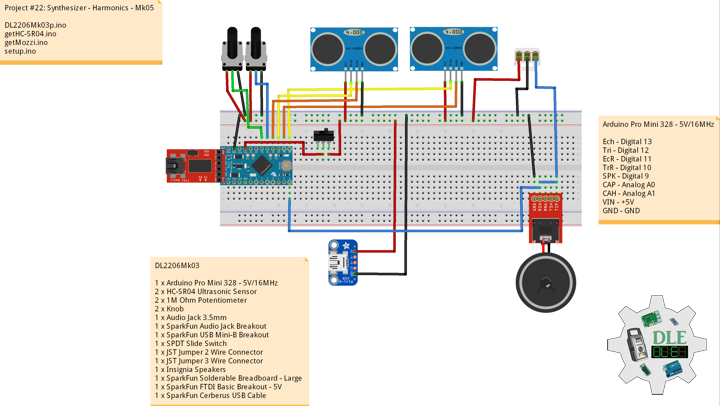
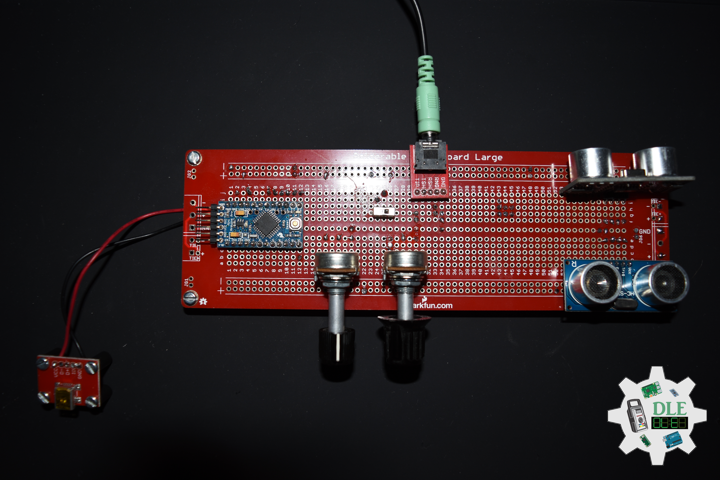
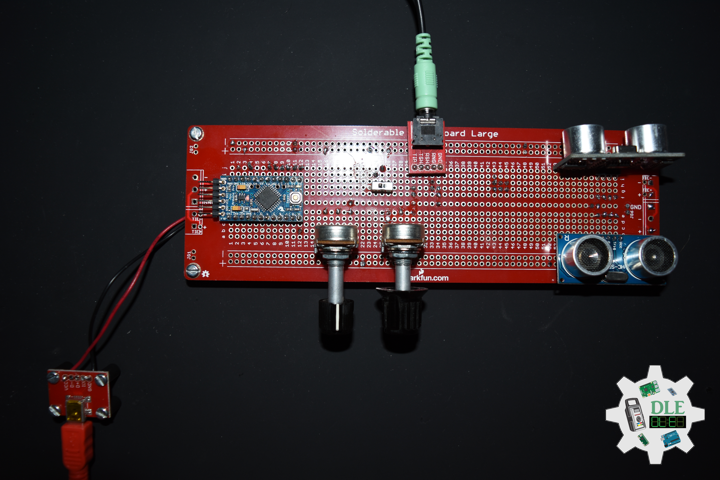
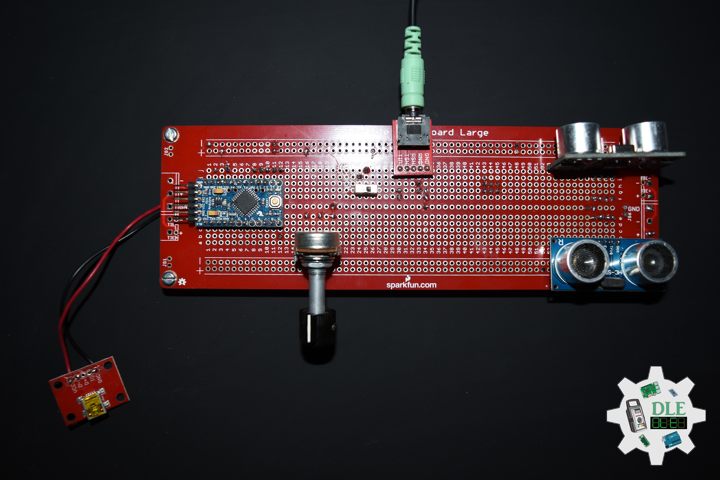
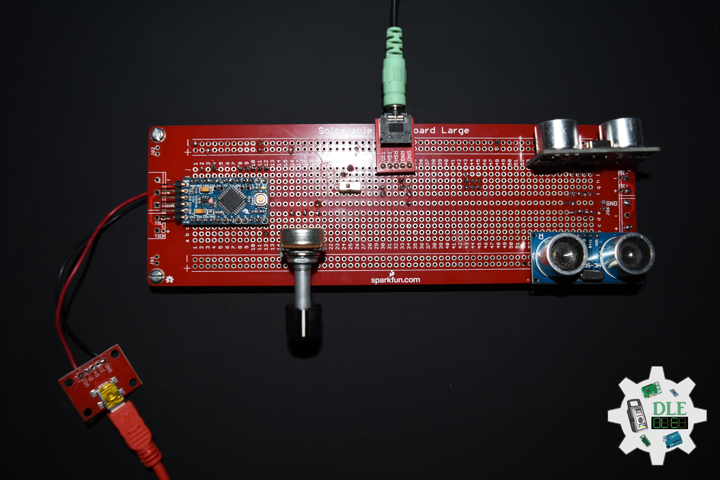
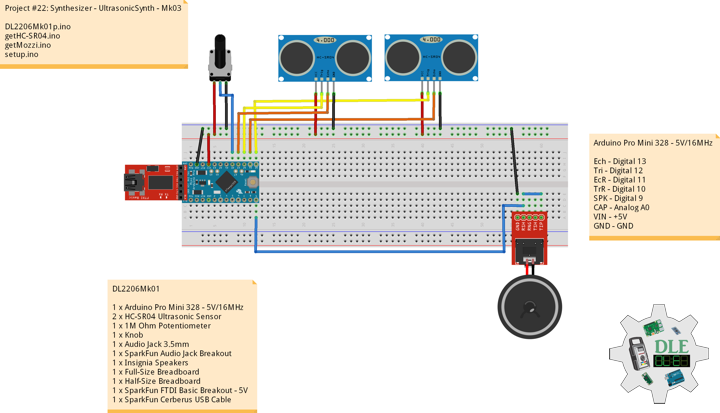
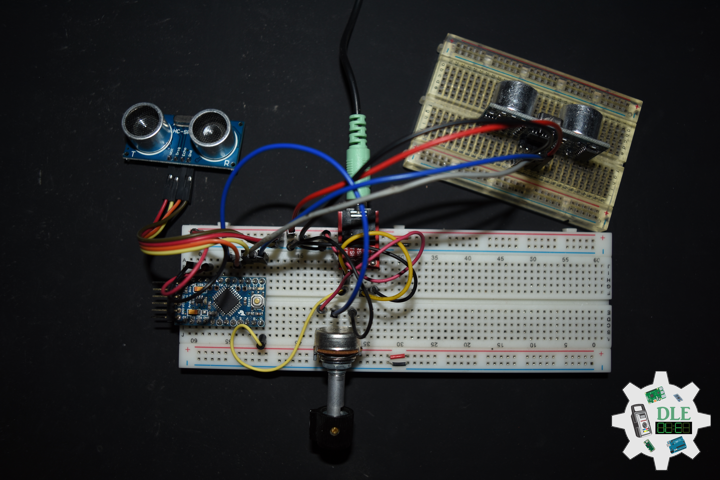
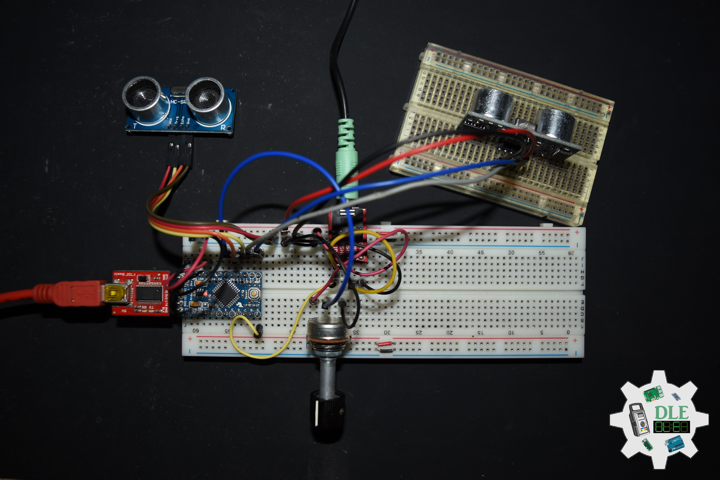
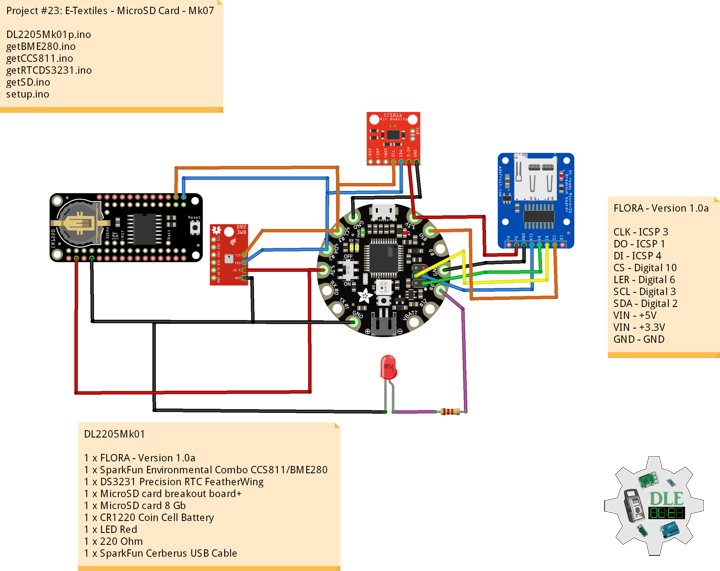
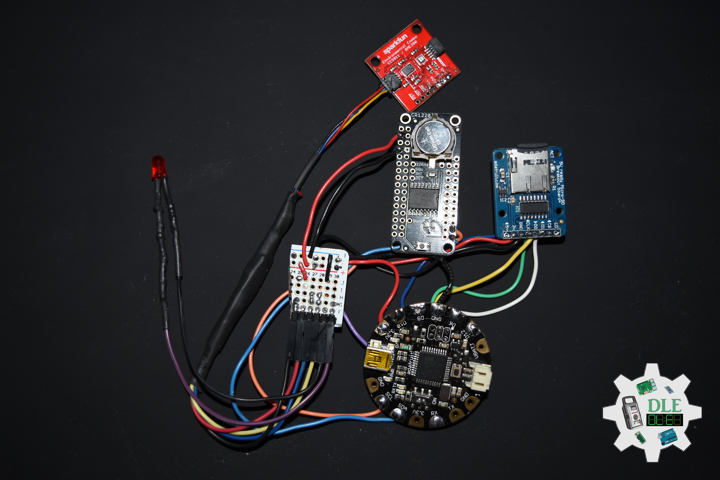
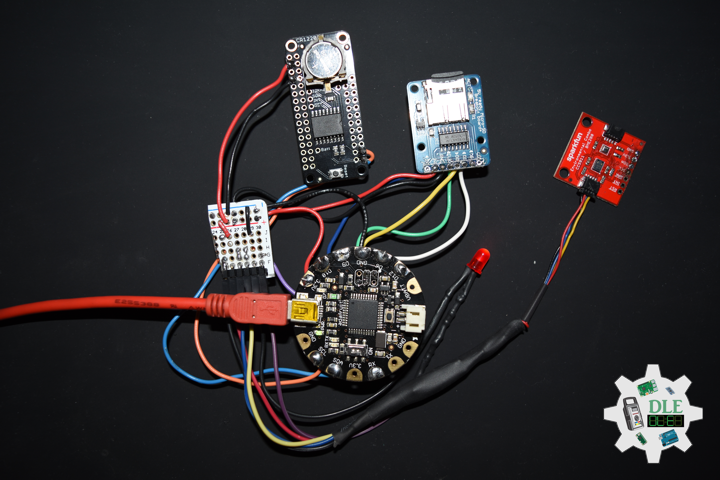
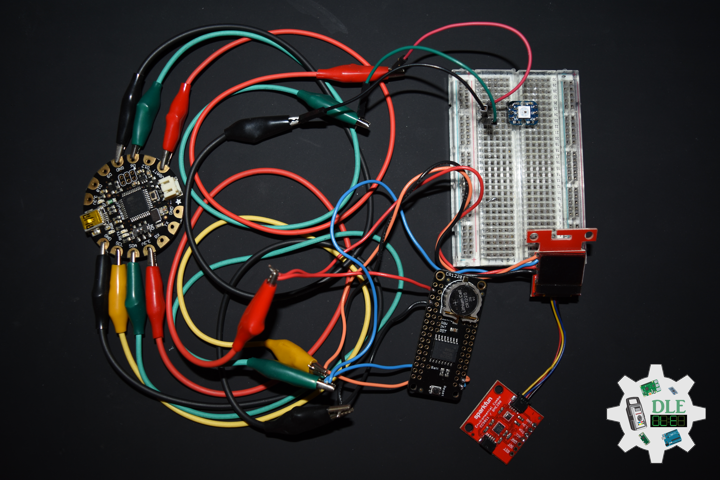
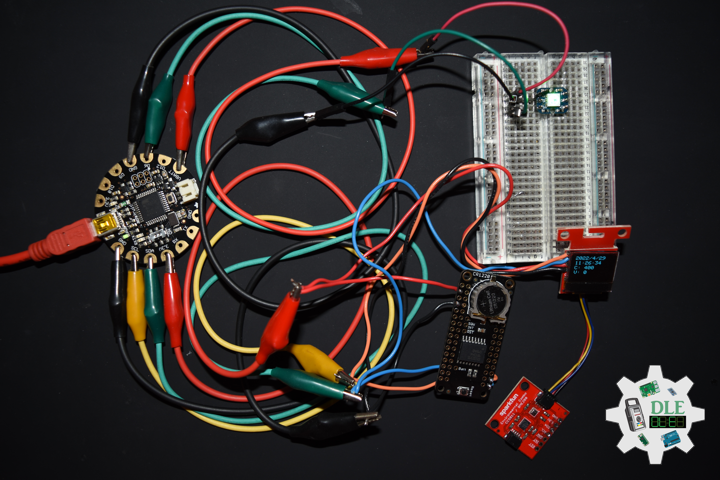
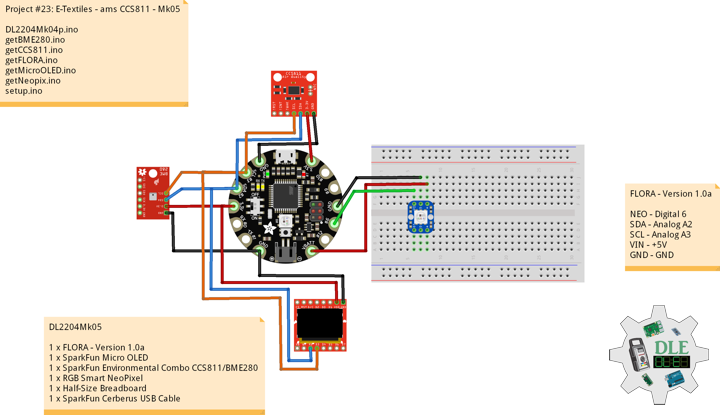
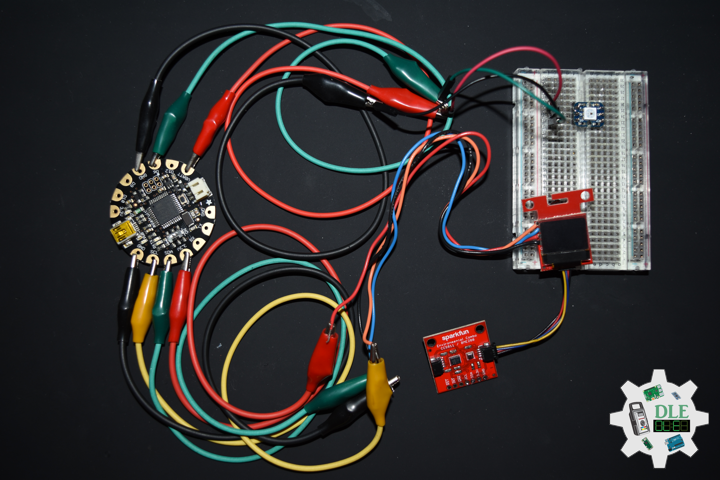
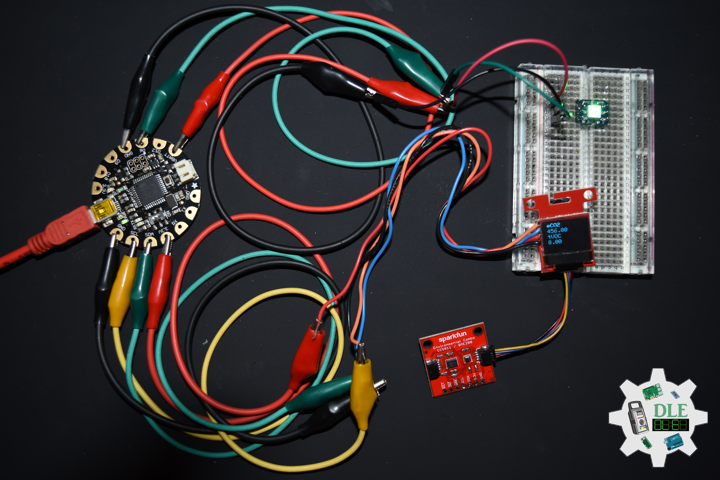
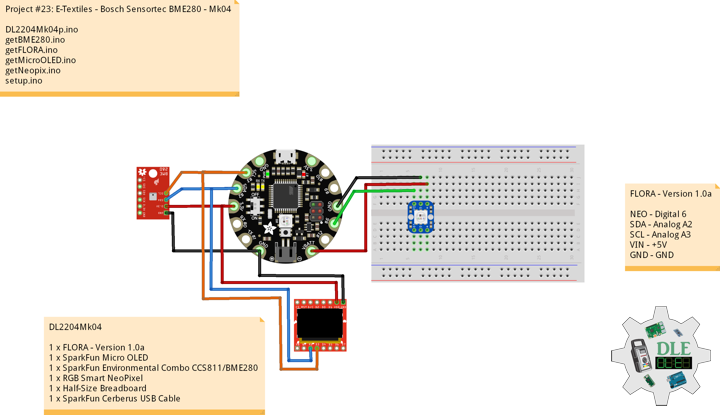
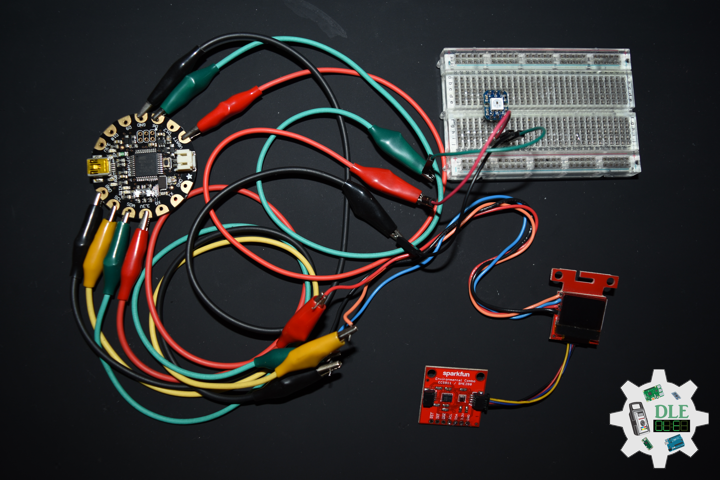
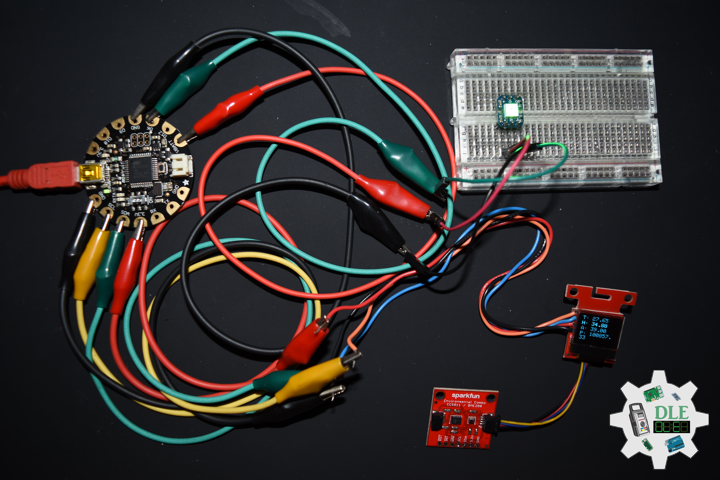
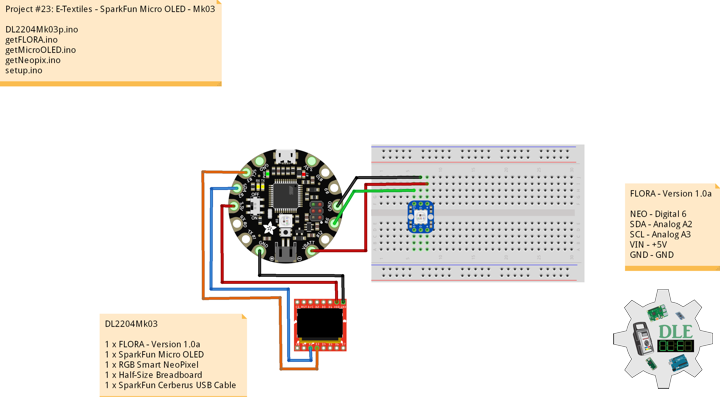
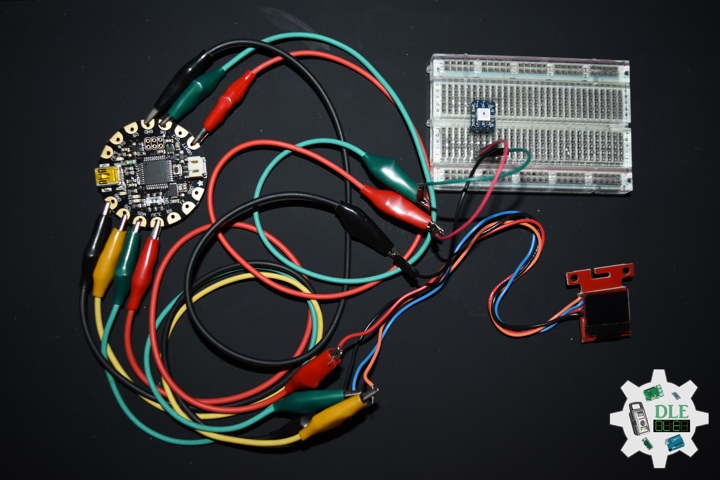
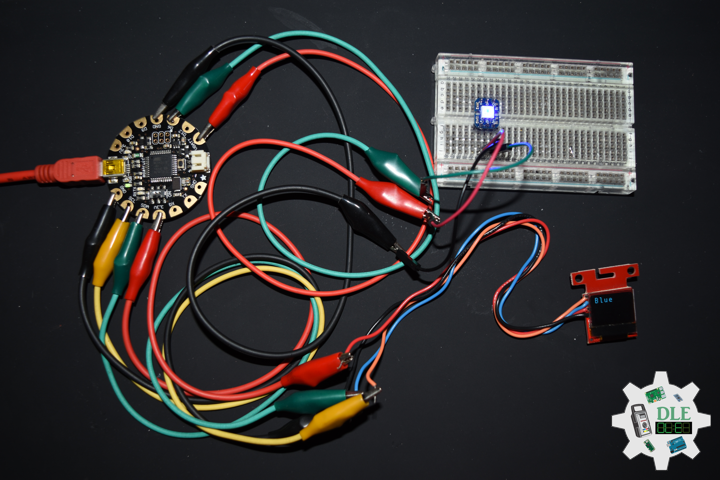
DL2207Mk01
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
8 x Tactile Button
3 x 1K Ohm Potentiometer
3 x Knob
1 x JST Jumper 3 Wire Connector
1 x Solderable Breadboard
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
KY2 – Digital 2
KY3 – Digital 3
KY4 – Digital 4
KY5 – Digital 5
KY6 – Digital 6
KY7 – Digital 7
KY8 – Digital 8
SPK – Digital 9
KY9 – Digital 10
PFR – Analog A3
CDE – Analog A2
CAT – Analog A1
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
DL2207Mk01p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #22: Synthesizer - Envelope - Mk06
22-06
DL2207Mk01p.ino
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 - 5V/16MHz
8 x Tactile Button
3 x 1K Ohm Potentiometer
3 x Knob
4 x SPDT Slide Switch
1 x JST Jumper 3 Wire
1 x Insignia Speakers
1 x Solderable Breadboard
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Pitches
#include "pitches.h"
// Mozzi
#include <MozziGuts.h>
// Oscillator
#include <Oscil.h>
// Table for Oscils to play
#include <tables/sin2048_int8.h>
// ADSR envelope generator
#include <ADSR.h>
// Simple Keyboard
// Minimum reading of the button that generates a note
const int iKeyboard2 = 2;
const int iKeyboard3 = 3;
const int iKeyboard4 = 4;
const int iKeyboard5 = 5;
const int iKeyboard6 = 6;
const int iKeyboard7 = 7;
const int iKeyboard8 = 8;
const int iKeyboard9 = 10;
// Button is pressed
int aa = 1;
int bb = 1;
int cc = 1;
int dd = 1;
int ee = 1;
int ff = 1;
int gg = 1;
int hh = 1;
//Oscillator Functions declared for output envelope 1
// Sine Wave
Oscil <2048, AUDIO_RATE> aSin1(SIN2048_DATA);
// ADSR declaration/definition
// Comment out to use control rate of 128
#define CONTROL_RATE 128
ADSR <CONTROL_RATE, CONTROL_RATE> envelope1;
// Set the input for the potentiometer Attack to analog pin 1
const int potAttack = A1;
// Attack
int attack_level = 0;
int iAttack = 0;
// Set the input for the potentiometer for Decay to analog pin 2
const int potDecay = A2;
// Decay
int decay_level = 0;
int iDecay = 0;
// Set the input for the potentiometer for Frequency to analog pin 3
const int potFreq = A3;
int iFreg = 1;
int iNoteA = 0;
int iNoteB = 0;
int iNoteC = 0;
int iNoteD = 0;
int iNoteE = 0;
int iNoteF = 0;
int iNoteG = 0;
int iNoteAA = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "22-06";
void loop() {
// Audio Hook
audioHook();
}
getKeyboard.ino
// getKeyboard
// setupKeyboard
void setupKeyboard() {
// Initialize the pushbutton pin as an input
pinMode(iKeyboard2, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard3, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard4, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard5, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard6, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard7, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard8, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(iKeyboard9, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
// isKeyboard
void isKeyboard() {
// Choose envelope levels
// attack_level
iAttack = mozziAnalogRead( potAttack );
attack_level = map( iAttack, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// decay_level
iDecay = mozziAnalogRead( potDecay );
decay_level = map( iDecay, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// set AD Levels
envelope1.setADLevels(attack_level,decay_level);
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard2) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
aa = aa + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteA);
}
else
{
aa = aa - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard3) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
bb = bb + 1;
// Waveform
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteB);
}
else
{
bb = bb - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard4) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
cc = cc + 1;
// Waveform
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteC);
}
else
{
cc = cc - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard5) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
dd = dd + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteD);
}
else
{
dd = dd - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard6) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
ee = ee + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteE);
}
else
{
ee = ee - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard7) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
ff = ff + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteF);
}
else
{
ff = ff - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard8) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
gg = gg + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteG);
}
else
{
gg = gg - 1;
}
// Read the state of the pushbutton value
if ( digitalRead(iKeyboard9) == LOW ) {
// Button is pressed - pullup keeps pin high normally
hh = hh + 1;
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.noteOn();
aSin1.setFreq(iNoteAA);
}
else
{
hh = hh - 1;
}
}
getMozzi.ino
// Mozzi
// Update Control
void updateControl(){
// Frequency
isPitches();
// Keyboard
isKeyboard();
}
// Update Audio
int updateAudio()
{
// Update Audio
// ADSR declaration/definition
envelope1.update();
// >>8 for AUDIO_MODE STANDARD
return (int) (envelope1.next() * aSin1.next())>>8;
}
getPitches.ino
// Pitches
// isPitches
void isPitches(){
// Frequency
// Value is 0-1023
iFreg = mozziAnalogRead(potFreq);
iFreg = map(iFreg, 0, 1023, 3, 6);
// Range Frequency Note Low => High
switch ( iFreg ) {
case 1:
// NOTE A1
iNoteA = NOTE_A1;
iNoteB = NOTE_B1;
iNoteC = NOTE_C2;
iNoteD = NOTE_D2;
iNoteE = NOTE_E2;
iNoteF = NOTE_F2;
iNoteG = NOTE_G2;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A2;
break;
case 2:
// NOTE A2
iNoteA = NOTE_A2;
iNoteB = NOTE_B2;
iNoteC = NOTE_C3;
iNoteD = NOTE_D3;
iNoteE = NOTE_E3;
iNoteF = NOTE_F3;
iNoteG = NOTE_G3;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A3;
break;
case 3:
// NOTE A3
iNoteA = NOTE_A3;
iNoteB = NOTE_B3;
iNoteC = NOTE_C4;
iNoteD = NOTE_D4;
iNoteE = NOTE_E4;
iNoteF = NOTE_F4;
iNoteG = NOTE_G4;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A4;
break;
case 4:
// NOTE A4
iNoteA = NOTE_A4;
iNoteB = NOTE_B4;
iNoteC = NOTE_C5;
iNoteD = NOTE_D5;
iNoteE = NOTE_E5;
iNoteF = NOTE_F5;
iNoteG = NOTE_G5;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A5;
break;
case 5:
// NOTE A5
iNoteA = NOTE_A5;
iNoteB = NOTE_B5;
iNoteC = NOTE_C6;
iNoteD = NOTE_D6;
iNoteE = NOTE_E6;
iNoteF = NOTE_F6;
iNoteG = NOTE_G6;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A6;
break;
case 6:
// NOTE A6
iNoteA = NOTE_A6;
iNoteB = NOTE_B6;
iNoteC = NOTE_C7;
iNoteD = NOTE_D7;
iNoteE = NOTE_E7;
iNoteF = NOTE_F7;
iNoteG = NOTE_G7;
iNoteAA = NOTE_A7;
break;
}
}
pitches.h
/***************************************************************** * Pitches NOTE_B0 <=> NOTE_DS8 - NOTE_A4 is "A" measured at 440Hz *****************************************************************/ #define NOTE_B0 31 #define NOTE_C1 33 #define NOTE_CS1 35 #define NOTE_D1 37 #define NOTE_DS1 39 #define NOTE_E1 41 #define NOTE_F1 44 #define NOTE_FS1 46 #define NOTE_G1 49 #define NOTE_GS1 52 #define NOTE_A1 55 #define NOTE_AS1 58 #define NOTE_B1 62 #define NOTE_C2 65 #define NOTE_CS2 69 #define NOTE_D2 73 #define NOTE_DS2 78 #define NOTE_E2 82 #define NOTE_F2 87 #define NOTE_FS2 93 #define NOTE_G2 98 #define NOTE_GS2 104 #define NOTE_A2 110 #define NOTE_AS2 117 #define NOTE_B2 123 #define NOTE_C3 131 #define NOTE_CS3 139 #define NOTE_D3 147 #define NOTE_DS3 156 #define NOTE_E3 165 #define NOTE_F3 175 #define NOTE_FS3 185 #define NOTE_G3 196 #define NOTE_GS3 208 #define NOTE_A3 220 #define NOTE_AS3 233 #define NOTE_B3 247 #define NOTE_C4 262 #define NOTE_CS4 277 #define NOTE_D4 294 #define NOTE_DS4 311 #define NOTE_E4 330 #define NOTE_F4 349 #define NOTE_FS4 370 #define NOTE_G4 392 #define NOTE_GS4 415 #define NOTE_A4 440 #define NOTE_AS4 466 #define NOTE_B4 494 #define NOTE_C5 523 #define NOTE_CS5 554 #define NOTE_D5 587 #define NOTE_DS5 622 #define NOTE_E5 659 #define NOTE_F5 698 #define NOTE_FS5 740 #define NOTE_G5 784 #define NOTE_GS5 831 #define NOTE_A5 880 #define NOTE_AS5 932 #define NOTE_B5 988 #define NOTE_C6 1047 #define NOTE_CS6 1109 #define NOTE_D6 1175 #define NOTE_DS6 1245 #define NOTE_E6 1319 #define NOTE_F6 1397 #define NOTE_FS6 1480 #define NOTE_G6 1568 #define NOTE_GS6 1661 #define NOTE_A6 1760 #define NOTE_AS6 1865 #define NOTE_B6 1976 #define NOTE_C7 2093 #define NOTE_CS7 2217 #define NOTE_D7 2349 #define NOTE_DS7 2489 #define NOTE_E7 2637 #define NOTE_F7 2794 #define NOTE_FS7 2960 #define NOTE_G7 3136 #define NOTE_GS7 3322 #define NOTE_A7 3520 #define NOTE_AS7 3729 #define NOTE_B7 3951 #define NOTE_C8 4186 #define NOTE_CS8 4435 #define NOTE_D8 4699 #define NOTE_DS8 4978
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Setup Keyboard
setupKeyboard();
// Mozzi Start
startMozzi( CONTROL_RATE );
// Sets Attack and Decay Levels; assumes Sustain, Decay, and Idle times
envelope1.setADLevels(200,200);
// Sets Decay time in milliseconds
envelope1.setDecayTime(100);
// Sustain Time setting for envelope1
envelope1.setSustainTime(32500);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc