——
#DonLuc #Environment #Microcontrollers #ESP32 #MQ #GPS #SparkFun #Adafruit #Pololu #Fritzing #Programming #Arduino #Electronics #Consultant #Vlog #Aphasia
——
——
——
——
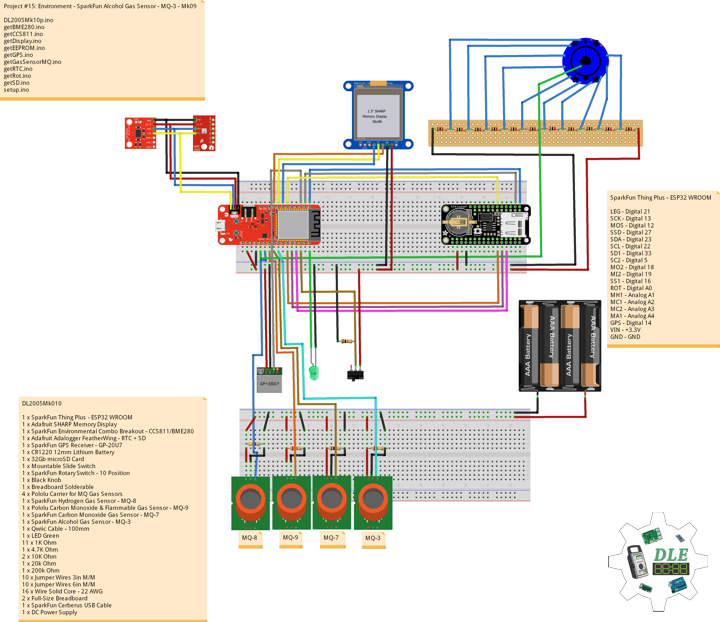
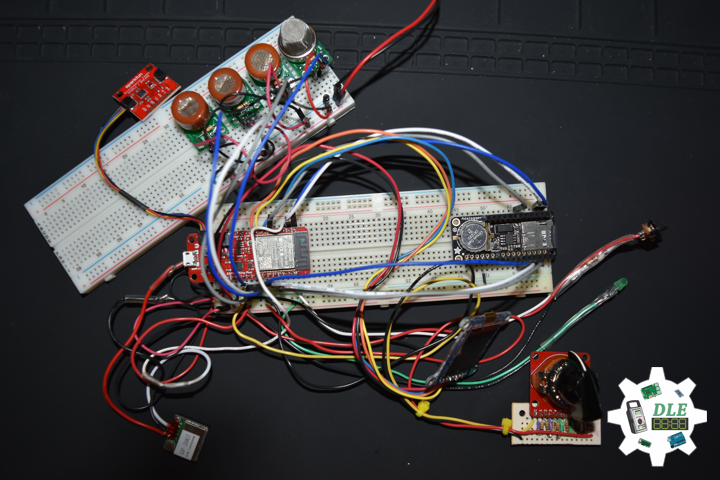
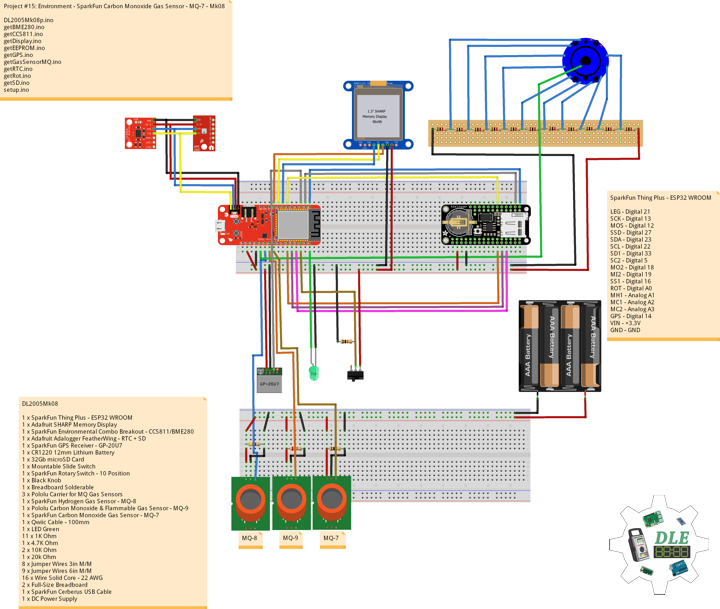
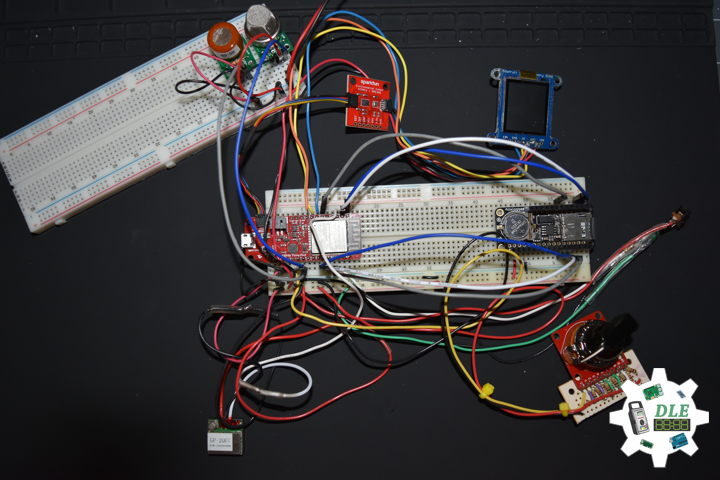
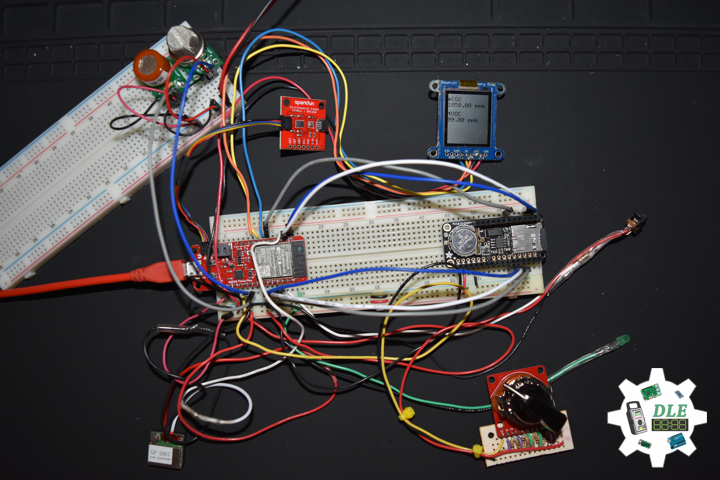
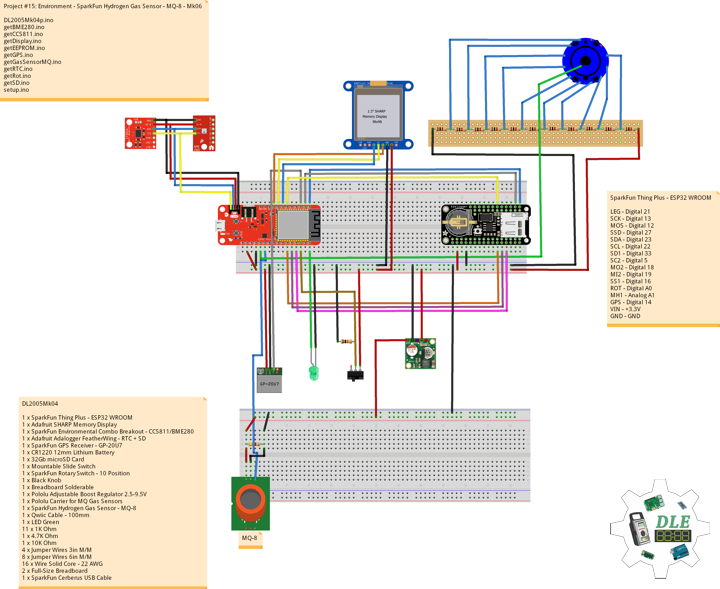
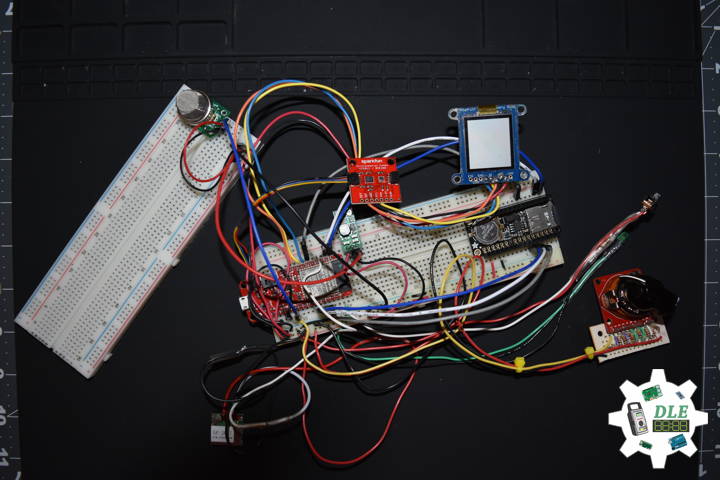
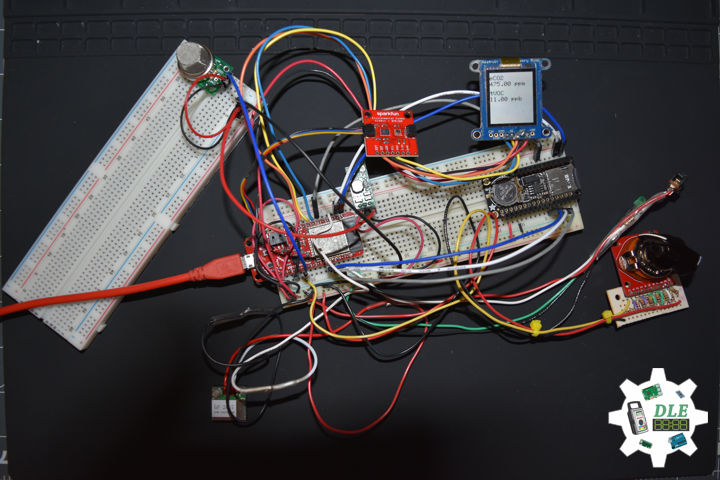
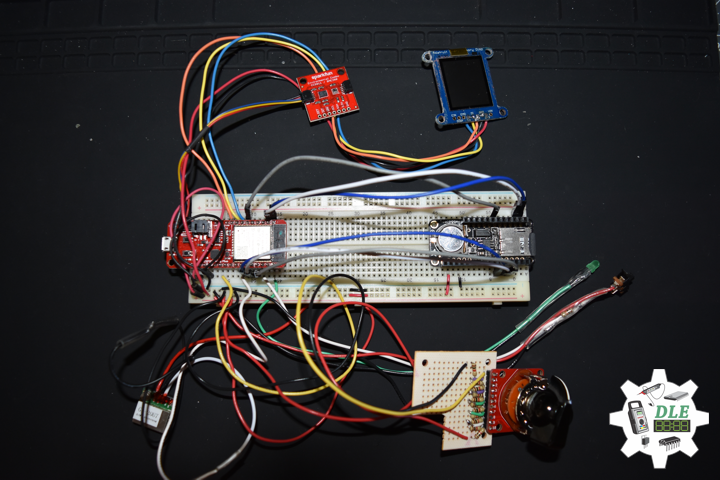
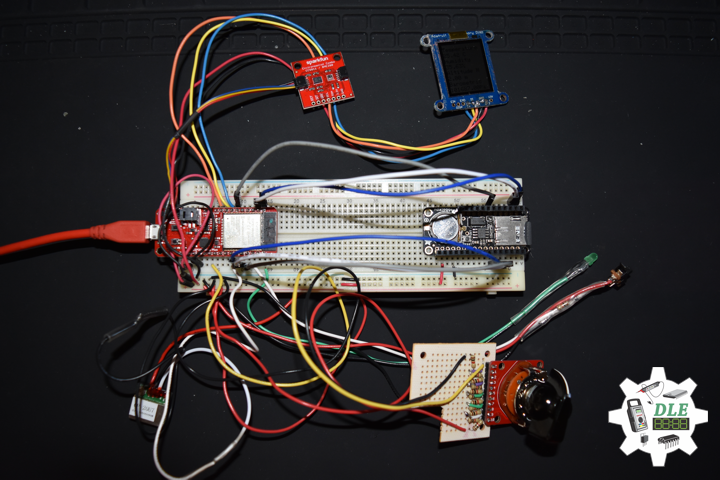
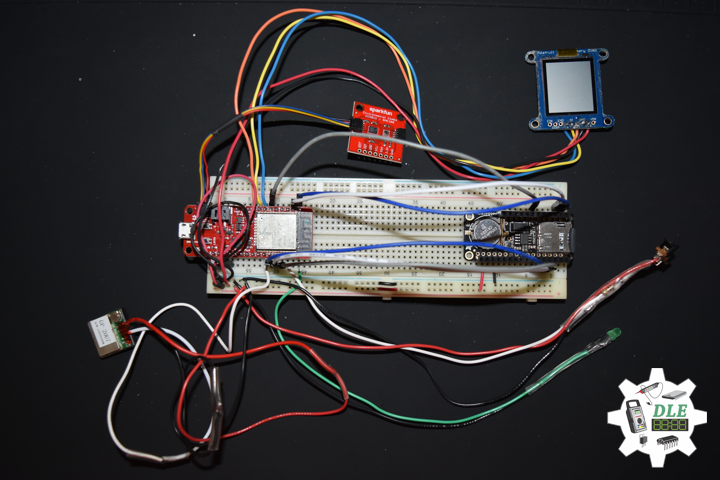
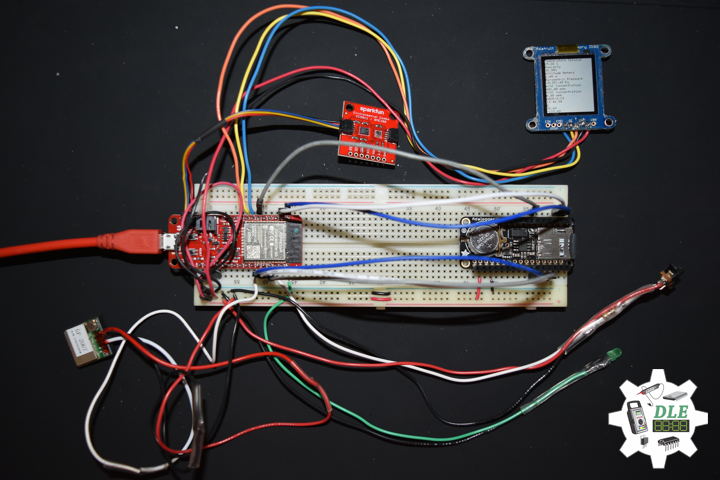
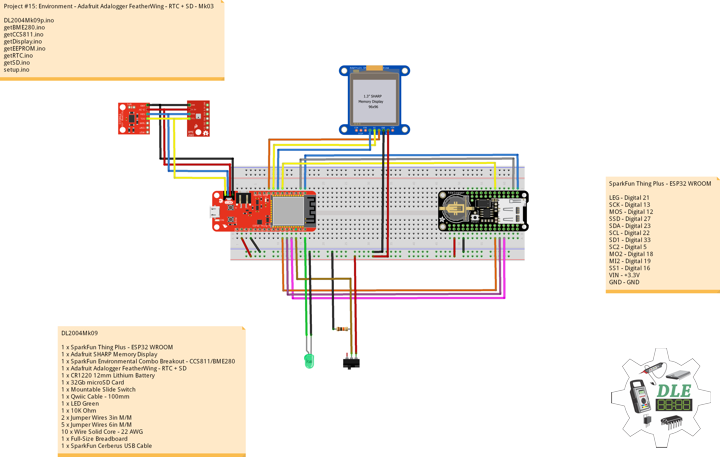
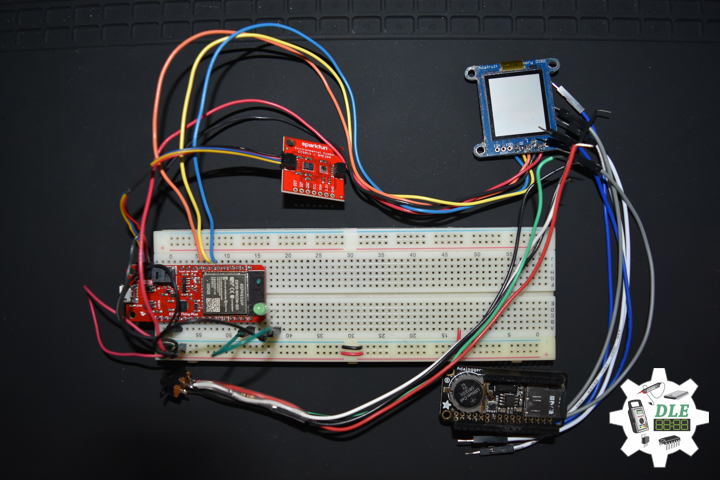
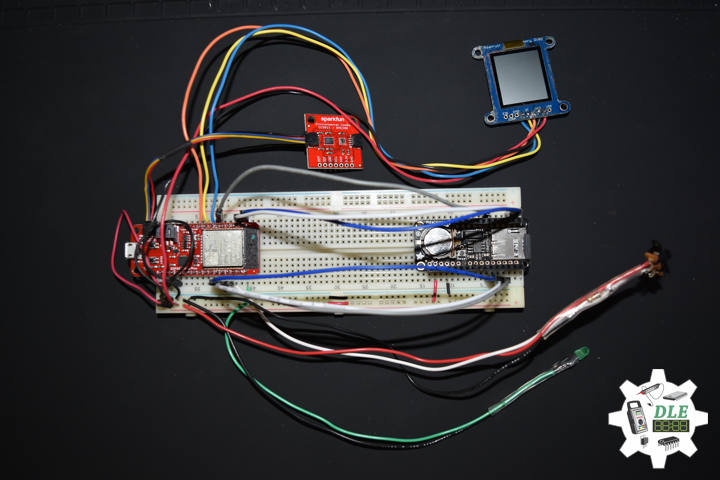
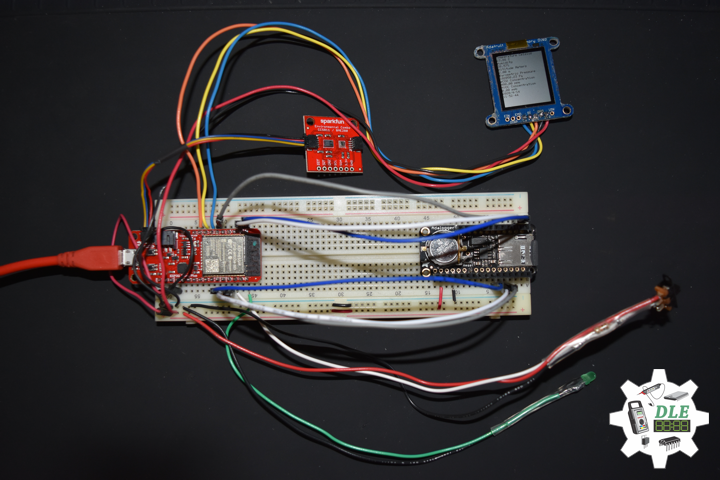
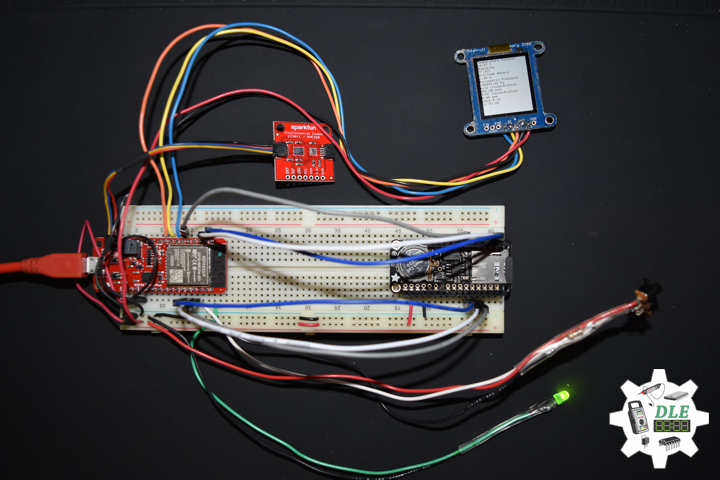
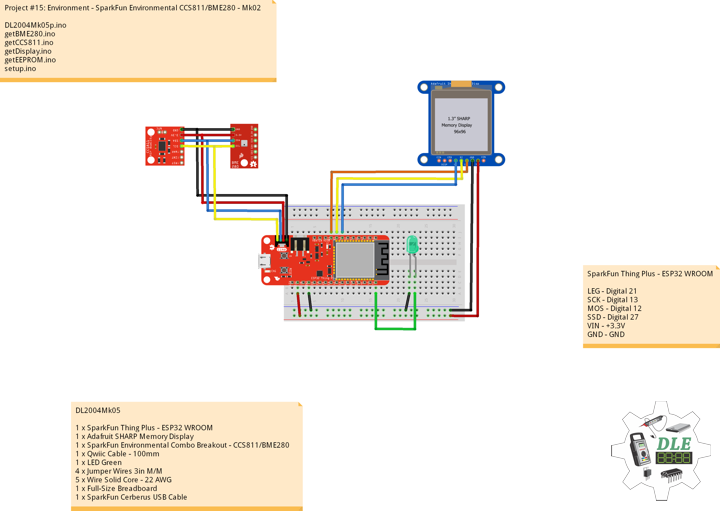
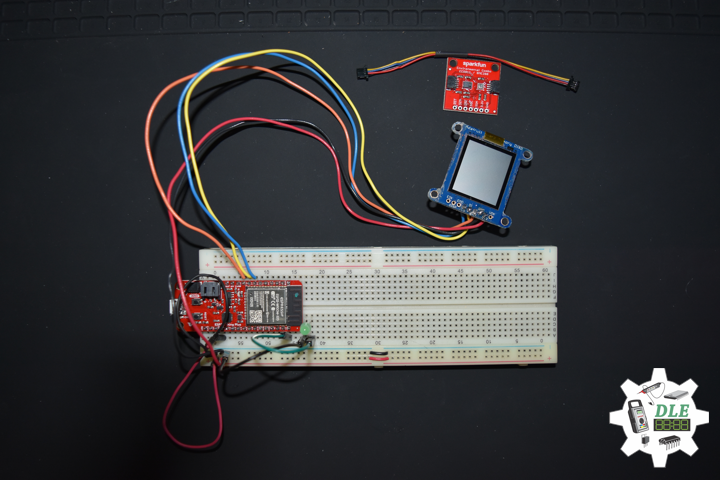
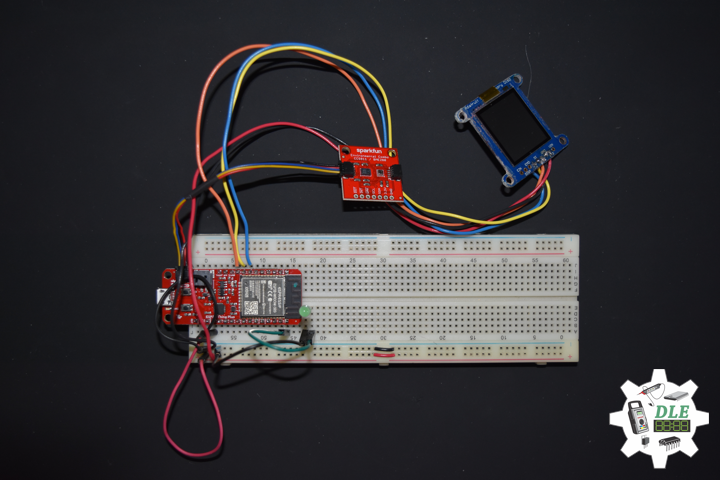
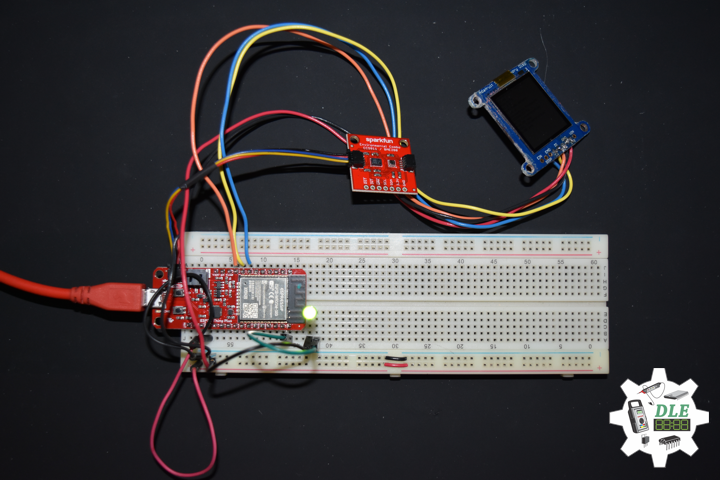
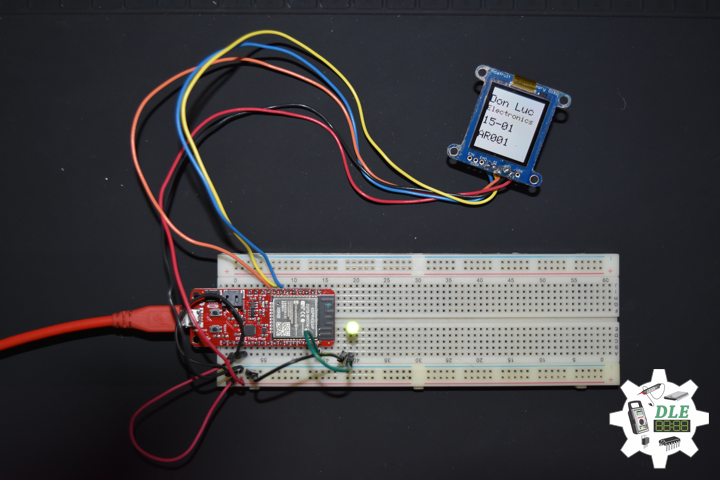
DL2005Mk010
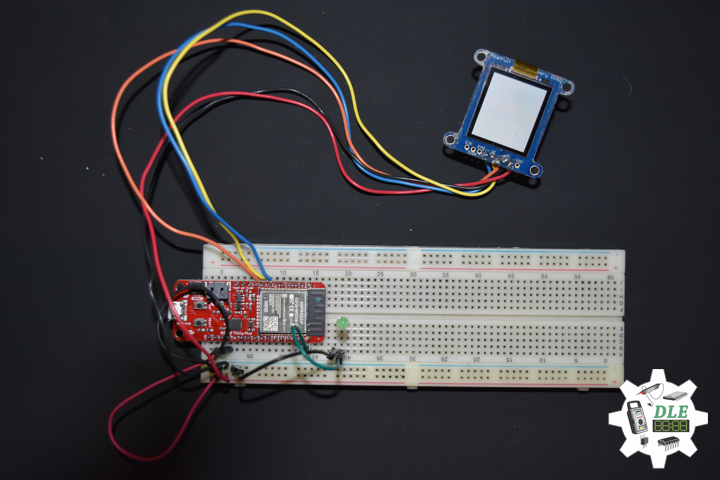
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x SparkFun Environmental Combo Breakout – CCS811/BME280
1 x Adafruit Adalogger FeatherWing – RTC + SD
1 x SparkFun GPS Receiver – GP-20U7
1 x CR1220 12mm Lithium Battery
1 x 32Gb microSD Card
1 x Mountable Slide Switch
1 x SparkFun Rotary Switch – 10 Position
1 x Black Knob
1 x Breadboard Solderable
4 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x SparkFun Hydrogen Gas Sensor – MQ-8
1 x Pololu Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor – MQ-9
1 x SparkFun Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor – MQ-7
1 x SparkFun Alcohol Gas Sensor – MQ-3
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x LED Green
11 x 1K Ohm
1 x 4.7K Ohm
2 x 10K Ohm
1 x 20k Ohm
1 x 220k Ohm
10 x Jumper Wires 3in M/M
10 x Jumper Wires 6in M/M
16 x Wire Solid Core – 22 AWG
2 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
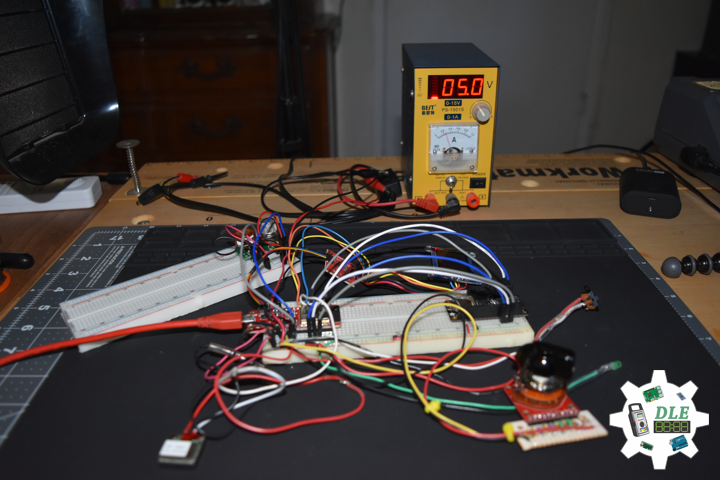
1 x DC Power Supply
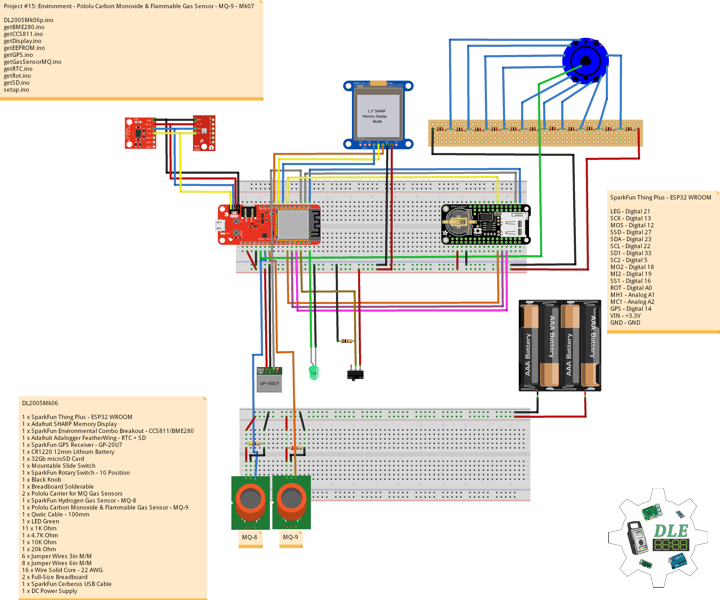
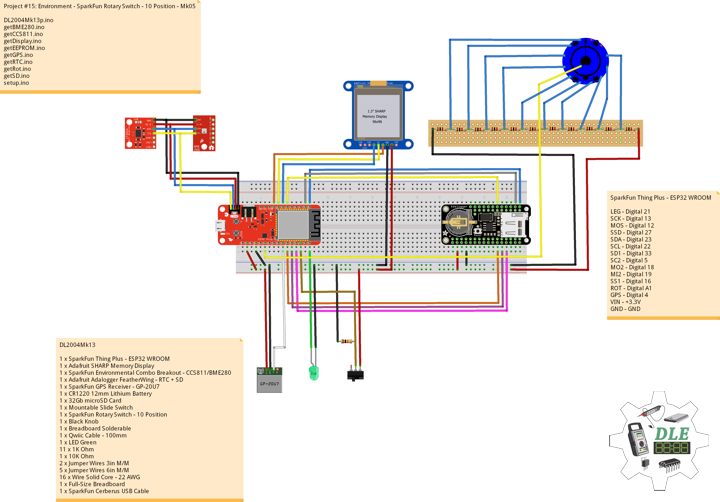
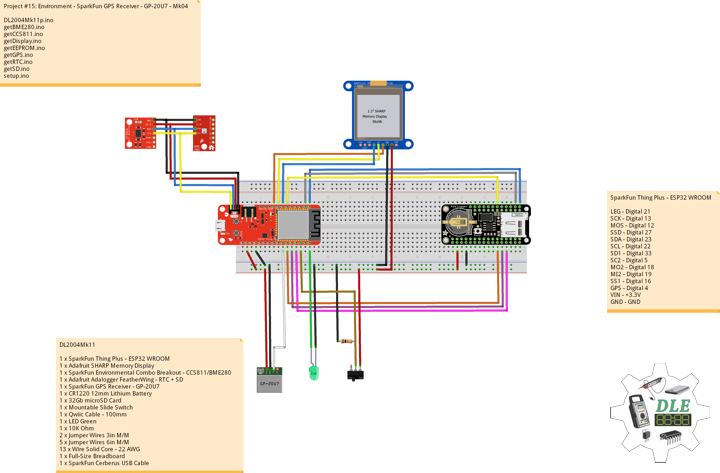
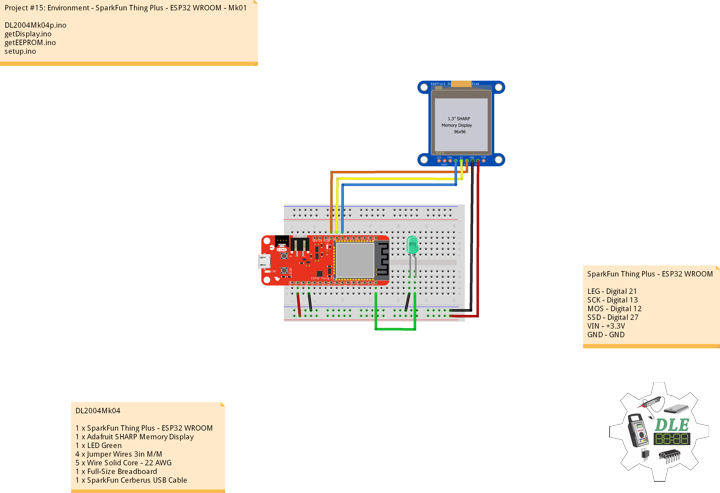
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
LEG – Digital 21
SCK – Digital 13
MOS – Digital 12
SSD – Digital 27
SDA – Digital 23
SCL – Digital 22
SD1 – Digital 33
SC2 – Digital 5
MO2 – Digital 18
MI2 – Digital 19
SS1 – Digital 16
ROT – Analog A1
MH1 – Analog A0
MC1 – Analog A2
MC2 – Analog A3
MA1 – Analog A4
GPS – Digital 14
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2005Mk10p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #15: Environment - SparkFun Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3 - Mk09
// 05-09
// DL2005Mk10p.ino 15-09
// EEPROM with Unique ID
// 1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
// 1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
// 1 x SparkFun Environmental Combo Breakout - CCS811/BME280
// 1 x Adafruit Adalogger FeatherWing - RTC + SD
// 1 x SparkFun GPS Receiver - GP-20U7
// 1 x CR1220 12mm Lithium Battery
// 1 x 32Gb microSD Card
// 1 x Mountable Slide Switch
// 1 x SparkFun Rotary Switch - 10 Position
// 1 x Black Knob
// 1 x Breadboard Solderable
// 4 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
// 1 x Pololu Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor - MQ-9
// 1 x SparkFun Hydrogen Gas Sensor - MQ-8
// 1 x SparkFun Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor - MQ-7
// 1 x SparkFun Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
// 1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
// 1 x LED Green
// 11 x 1K Ohm
// 1 x 4.7K Ohm
// 1 x 10K Ohm
// 1 x 20K Ohm
// 1 x 220k Ohm
// 10 x Jumper Wires 3in M/M
// 10 x Jumper Wires 6in M/M
// 16 x Wire Solid Core - 22 AWG
// 2 x Full-Size Breadboard
// 1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
// 1 x DC Power Supply
// Include the Library Code
// EEPROM Library to Read and Write EEPROM with Unique ID for Unit
#include "EEPROM.h"
// Wire
#include <Wire.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
#include <Adafruit_SharpMem.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
#include <SparkFunCCS811.h>
// SparkFun BME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
#include <SparkFunBME280.h>
// Date and Time
#include "RTClib.h"
// SD Card
#include "FS.h"
#include "SD.h"
#include "SPI.h"
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
// Hardware Serial
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// LED Green
int iLEDGreen = 21;
// SHARP Memory Display
// any pins can be used
#define SHARP_SCK 13
#define SHARP_MOSI 12
#define SHARP_SS 27
// Set the size of the display here - 144x168
Adafruit_SharpMem display(SHARP_SCK, SHARP_MOSI, SHARP_SS, 144, 168);
// The currently-available SHARP Memory Display (144x168 pixels)
// requires > 4K of microcontroller RAM; it WILL NOT WORK on Arduino Uno
// or other <4K "classic" devices!
#define BLACK 0
#define WHITE 1
// 1/2 of lesser of display width or height
int minorHalfSize;
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
// Default I2C Address
#define CCS811_ADDR 0x5B
CCS811 myCCS811(CCS811_ADDR);
float CCS811CO2 = 0;
float CCS811TVOC = 0;
// SparkFun BME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
BME280 myBME280;
float BMEtempC = 0;
float BMEhumid = 0;
float BMEaltitudeM = 0;
float BMEpressure = 0;
// Date and Time
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
RTC_PCF8523 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// microSD Card
const int chipSelect = 33;
String zzzzzz = "";
// Mountable Slide Switch
int iSS1 = 16;
// State
int iSS1State = 0;
// ESP32 HardwareSerial
HardwareSerial tGPS(2);
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 14
// This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
#define gpsTXPIN 32
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
float TargetLat;
float TargetLon;
int GPSStatus = 0;
// Rotary Switch - 10 Position
// Number 1 => 10
int iRotNum = A0;
// iRotVal - Value
int iRotVal = 0;
// Number
int z = 0;
int x = 0;
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Hydrogen Gas Sensor - MQ-8
int iMQ8 = A1;
int iMQ8Raw = 0;
int iMQ8ppm = 0;
// Two points are taken from the curve in datasheet
// With these two points, a line is formed which is "approximately equivalent" to the original curve
float H2Curve[3] = {2.3, 0.93,-1.44};
// Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor - MQ-9
int iMQ9 = A2;
int iMQ9Raw = 0;
int iMQ9ppm = 0;
// Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor - MQ-7
int iMQ7 = A3;
int iMQ7Raw = 0;
int iMQ7ppm = 0;
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int iMQ3 = A4;
int iMQ3Raw = 0;
int iMQ3ppm = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "15-09";
// EEPROM Unique ID Information
#define EEPROM_SIZE 64
String uid = "";
void loop() {
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
isGPS();
// Date and Time
isRTC();
// SparkFun BME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
isBME280();
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
isCCS811();
// Gas Sensors MQ
isGasSensor();
// Rotary Switch
isRot();
// Slide Switch
// Read the state of the iSS1 value
iSS1State = digitalRead(iSS1);
// If it is the Slide Switch State is HIGH
if (iSS1State == HIGH) {
// iLEDGreen
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, HIGH );
// microSD Card
isSD();
} else {
// iLEDGreen
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, LOW );
}
delay( 1000 );
}
getBME280.ino
// SparkFun BME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
// isBME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
void isBME280(){
// Temperature Celsius
BMEtempC = myBME280.readTempC();
// Humidity
BMEhumid = myBME280.readFloatHumidity();
// Altitude Meters
BMEaltitudeM = (myBME280.readFloatAltitudeMeters(), 2);
// Barometric Pressure
BMEpressure = myBME280.readFloatPressure();
}
getCCS811.ino
// CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
// isCCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
void isCCS811(){
// This sends the temperature & humidity data to the CCS811
myCCS811.setEnvironmentalData(BMEhumid, BMEtempC);
// Calling this function updates the global tVOC and eCO2 variables
myCCS811.readAlgorithmResults();
// eCO2 Concentration
CCS811CO2 = myCCS811.getCO2();
// tVOC Concentration
CCS811TVOC = myCCS811.getTVOC();
}
getDisplay.ino
// Display
// SHARP Memory Display - UID
void isDisplayUID() {
// Text Display
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Don Luc Electronics
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "Don Luc" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,40);
display.println( "Electronics" );
// Version
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.println( "Version" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( sver );
// EEPROM Unique ID
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(0,130);
display.println( "EEPROM Unique ID" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,145);
display.println( uid );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Environmental
void isDisplayEnvironmental(){
// Text Display Environmental
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Temperature Celsius
display.setCursor(0,0);
display.println( "Temperature Celsius" );
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.print( BMEtempC );
display.println( " C" );
// Humidity
display.setCursor(0,20);
display.println( "Humidity" );
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.print( BMEhumid );
display.println( "%" );
// Altitude Meters
display.setCursor(0,40);
display.println( "Altitude Meters" );
display.setCursor(0,50);
display.print( BMEaltitudeM );
display.println( " m" );
// Pressure
display.setCursor(0,60);
display.println( "Barometric Pressure" );
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.print( BMEpressure );
display.println( " Pa" );
// eCO2 Concentration
display.setCursor(0,80);
display.println( "eCO2 Concentration" );
display.setCursor(0,90);
display.print( CCS811CO2 );
display.println( " ppm" );
// tVOC Concentration
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( "tVOC Concentration" );
display.setCursor(0,110);
display.print( CCS811TVOC );
display.println( " ppb" );
// Date
display.setCursor(0,120);
display.println( dateRTC );
// Time
display.setCursor(0,130);
display.println( timeRTC );
// GPS Status
display.setCursor(0,140);
display.println( GPSStatus );
// Target Latitude
display.setCursor(0,150);
display.println( TargetLat );
// Target Longitude
display.setCursor(0,160);
display.println( TargetLon );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Date
void isDisplayDate() {
// Text Display Date
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Date
display.setCursor(0,5);
display.println( dateRTC );
// Time
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.println( timeRTC );
// GPS Status
display.setCursor(0,60);
display.print( "GPS: " );
display.println( GPSStatus );
// Target Latitude
display.setCursor(0,80);
display.println( "Latitude" );
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( TargetLat );
// Target Longitude
display.setCursor(0,120);
display.println( "Longitude" );
display.setCursor(0,140);
display.println( TargetLon );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display BME280
void isDisplayBME280() {
// Text Display BME280
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Temperature Celsius
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "Temperature" );
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.print( BMEtempC );
display.println( " C" );
// Humidity
display.setCursor(0,50);
display.println( "Humidity" );
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.print( BMEhumid );
display.println( "%" );
// Altitude Meters
display.setCursor(0,90);
display.println( "Altitude M" );
display.setCursor(0,110);
display.print( BMEaltitudeM );
display.println( " m" );
// Pressure
display.setCursor(0,130);
display.println( "Barometric" );
display.setCursor(0,150);
display.print( BMEpressure );
display.println( "Pa" );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
void isDisplayCCS811() {
// Text Display CCS811
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// eCO2 Concentration
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "eCO2" );
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.print( CCS811CO2 );
display.println( " ppm" );
// tVOC Concentration
display.setCursor(0,60);
display.println( "tVOC" );
display.setCursor(0,80);
display.print( CCS811TVOC );
display.println( " ppb" );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Gas Sensors MQ
void isDisplayMQ() {
// Text Display MQ
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Gas Sensors MQ
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "Gas H2 MQ8" );
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.print( iMQ8ppm );
display.println( " ppm" );
display.setCursor(0,50);
display.println( "Gas CO MQ9" );
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.print( iMQ9ppm );
display.println( " ppm" );
display.setCursor(0,90);
display.println( "Gas CO MQ7" );
display.setCursor(0,110);
display.print( iMQ7ppm );
display.println( " ppm" );
display.setCursor(0,130);
display.println( "BAC MQ3" );
display.setCursor(0,150);
display.print( iMQ3ppm );
display.println( "%" );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Z
void isDisplayZ() {
// Text Display Z
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Z
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.print( "Z: " );
display.println( z );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
getEEPROM.ino
// EEPROM
// isUID EEPROM Unique ID
void isUID()
{
// Is Unit ID
uid = "";
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++)
{
uid = uid + char(EEPROM.read(x));
}
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
void setupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 , SERIAL_8N1, gpsRXPIN, gpsTXPIN );
}
// isGPS
void isGPS(){
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
displayInfo();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo(){
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
GPSStatus = 2;
}
else
{
GPSStatus = 0;
}
}
getGasSensorMQ.ino
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Gas Sensor
void isGasSensor() {
// Read in analog value from each gas sensors
// Hydrogen Gas Sensor - MQ-8
iMQ8Raw = analogRead( iMQ8 );
// Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor - MQ-9
iMQ9Raw = analogRead( iMQ9 );
// Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor - MQ-7
iMQ7Raw = analogRead( iMQ7 );
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
iMQ3Raw = analogRead( iMQ3 );
// Caclulate the PPM of each gas sensors
// Hydrogen Gas Sensor - MQ-8
iMQ8ppm = isMQ8( iMQ8Raw );
// Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor - MQ-9
iMQ9ppm = isMQ9( iMQ9Raw );
// Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor - MQ-7
iMQ7ppm = isMQ7( iMQ7Raw );
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
iMQ3ppm = isMQ3( iMQ3Raw );
}
// Hydrogen Gas Sensor - MQ-8 - PPM
int isMQ8(double rawValue) {
// RvRo
double RvRo = rawValue * (3.3 / 1023);
return (pow(4.7,( ((log(RvRo)-H2Curve[1])/H2Curve[2]) + H2Curve[0])));
}
// Carbon Monoxide & Flammable Gas Sensor - MQ-9
int isMQ9(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue * (3.3 / 4095);
double ppm = 3.027*exp(1.0698*( RvRo ));
return ppm;
}
// Carbon Monoxide Gas Sensor - MQ-7
int isMQ7(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue * (3.3 / 4095);
double ppm = 3.027*exp(1.0698*( RvRo ));
return ppm;
}
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int isMQ3(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue * (3.3 / 4095);
double bac = RvRo * 0.21;
return bac;
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// Date & Time
// pcf8523 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
while (1);
}
if (! rtc.initialized()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
// rtc.adjust(DateTime(2018, 9, 29, 12, 17, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
}
getRot.ino
// Rotary Switch
// isRot - iRotVal - Value
void isRot() {
// Rotary Switch
z = analogRead( iRotNum );
x = map(z, 0, 4095, 0, 9);
iRotVal = map(z, 0, 4095, 0, 10);
// Range Value
switch ( iRotVal ) {
case 0:
// Display Environmental
isDisplayEnvironmental();
break;
case 1:
// Display Date
isDisplayDate();
break;
case 2:
// Display BME280
isDisplayBME280();
break;
case 3:
// Display CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
isDisplayCCS811();
break;
case 4:
// Display Gas Sensors MQ
isDisplayMQ();
break;
case 5:
// Display UID
isDisplayUID();
break;
case 6:
// Z
isDisplayZ();
break;
case 7:
// Z
isDisplayZ();
break;
case 8:
// Z
isDisplayZ();
break;
case 9:
// Z
isDisplayZ();
break;
}
}
getSD.ino
// microSD Card
// microSD Setup
void setupSD() {
// microSD Card
pinMode( chipSelect , OUTPUT );
if(!SD.begin( chipSelect )){
;
return;
}
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
;
return;
}
//Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
;
} else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
;
} else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
;
} else {
;
}
uint64_t cardSize = SD.cardSize() / (1024 * 1024);
}
// microSD Card
void isSD() {
zzzzzz = "";
// EEPROM Unique ID|Version|Date|Time|GPS Status|Target Latitude|Target Longitude|Temperature Celsius|Humidity|Altitude Meters|Barometric Pressure|eCO2 Concentration|tVOC Concentration|H2 Gas Sensor MQ-8|CO Gas Sensor MQ-9|CO Gas Sensor MQ-7|Alcohol Gas Sensor MQ-3
zzzzzz = uid + "|" + sver + "|" + dateRTC + "|" + timeRTC + "|" + GPSStatus + "|" + TargetLat + "|" + TargetLon + "|" + BMEtempC + "|" + BMEhumid + "|" + BMEaltitudeM + "|" + BMEpressure + "|" + CCS811CO2 + "|" + CCS811TVOC + "|" + iMQ8ppm + "|" + iMQ9ppm + "|" + iMQ7ppm + "|" + iMQ9ppm + "|" + iMQ3ppm + "|\r";
char msg[zzzzzz.length() + 1];
zzzzzz.toCharArray(msg, zzzzzz.length() + 1);
appendFile(SD, "/espdata.txt", msg );
}
// List Dir
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels){
dirname;
File root = fs.open(dirname);
if(!root){
return;
}
if(!root.isDirectory()){
return;
}
File file = root.openNextFile();
while(file){
if(file.isDirectory()){
file.name();
if(levels){
listDir(fs, file.name(), levels -1);
}
} else {
file.name();
file.size();
}
file = root.openNextFile();
}
}
// Write File
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
path;
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
;
} else {
;
}
file.close();
}
// Append File
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
path;
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
if(!file){
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
;
} else {
;
}
file.close();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// EEPROM Size
EEPROM.begin(EEPROM_SIZE);
// EEPROM Unique ID
isUID();
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
setupGPS();
// SHARP Display Start & Clear the Display
display.begin();
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
// Display UID
isDisplayUID();
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// SparkFun BME280 - Humidity, Temperature, Altitude and Barometric Pressure
myBME280.begin();
// CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
myCCS811.begin();
// Initialize the LED Green
pinMode(iLEDGreen, OUTPUT);
// Date & Time RTC
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Date & Time
isRTC();
// microSD Card
setupSD();
// Slide Switch
pinMode(iSS1, INPUT);
delay( 5000 );
}
Technology Experience
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
- Robotics
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
Follow Us
The Alpha Geek
Aphasia
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae
https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/LucPaquinCVEngMk2020a.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Don Luc